As part of the MetriQs-France programme, the quantum metrology platform MetriQs-France brings together state-of-the-art equipment, excellent experimental conditions and unique metrology expertise. It is used for R&D work and offers industrial and academic players measurement services adapted to quantum technologies.
The platform is hosted by laboratories of the French National Metrology Network (RNMF), i.e. LNE-OP within the Laboratoire Temps Espace (LTE) of the Observatoire de Paris - PSL, LNE-CNAM at Cnam (Conservatoire National des Arts et Métiers), and LNE (Laboratoire national de métrologie et d’essais). The MetriQs-France platform aims to constitute a reference metrology platform for quantum technologies, which is expert and independent, and active at the forefront internationally.
In summary
MetriQs-HUB-France is one of two components of the MetriQs-France programme, funded as part of the French National Strategy for Quantum Technologies (SNQ).With a budget of approximately €4 million, its primary objective is the deployment and implementation of a quantum metrology platform, enabling reliable, objective and comparable measurements of the characteristics and performance of equipment or instruments based on quantum technologies.
Hosted by laboratories of the French National Metrology Network (RNMF), the MetriQs-France platform relies on cutting-edge equipment, well-controlled experimental conditions, and expert metrology personnel. It aims to become a truly expert and independent reference platform, active on a national and international scale.
Given the exploratory nature of developments in this technological field, the MetriQs-France platform is intended to be open to academic and industrial users, thus meeting the testing and measurement needs of stakeholders in the quantum technology ecosystem. It also contributes to the development and promotion of measurement benchmarks developed as part of R&D projects funded by the MetriQs-France programme (MOCQUA and QUBE) in the areas of excellence of LNE and the RNMF.
The MetriQs-France platform comprises four thematic poles focused on:
- Characterisation of solid-state qubits and enabling technologies (RF electronics and cryogenics).
- Very low-temperature thermometry.
- Characterisation of quantum gravimeters.
- Characterisation of atomic clocks.
Metrology in support of innovation and industrialisation
To enable France to become a major player in the industrial deployment of quantum technologies, the French National Strategy for Quantum Technologies (SNQ) provides for extensive work to develop and promote objective, harmonised, and recognised measurement standards to enable the reliable, independent, and impartial characterisation of the performance of products and equipment based on these new cutting-edge technologies.
To this end, the French government entrusted LNE with the task of coordinating these activities and conducting them in close collaboration with national research organisations, French industrialists in the sector (start-ups, SMEs, mid-cap companies, large groups), AFNOR (French Standardisation Association) for standardisation, and its partners in the French National Metrology Network (RNMF) operating in the quantum field.
As part of the MetriQs-France programme, the quantum metrology platform MetriQs-France :
- Brings together the unique metrology expertise and state-of-the-art fundamental metrology facilities of LNE, LNE-CNAM at Cnam (Conservatoire National des Arts et Métiers), and LNE-OP within the Laboratoire Temps Espace (LTE) of Observatoire de Paris - PSL .
- Provides access to cutting-edge equipment and controlled experimental environments to public research players and industrialists in the quantum ecosystem in order to help them limit their investment risks in these emerging technologies, whose level of maturity is still low.
- Enables reliable, objective and comparable measurements of the characteristics and performance of quantum technology-based products and equipment, at the highest metrological level and with validated and harmonised measurement methods.
- Contributes to promoting and disseminating specific measurement standards by participating in standardisation work and ultimately developing new measurement, testing and calibration services, in support of industrialisation and commercialisation of quantum technologies.
- Is fully in with an international cooperation approach by getting involved in other initiatives led by the most advanced foreign national metrology institutes in this field, such as PTB in Germany, INRIM in Italy, NPL in the United Kingdom, NIST in the United States and NMIJ in Japan.
- Creates synergies between the measurement and characterisation means available in Europe through the EMN-Q network (European Metrology Network on Quantum Technologies) within EURAMET, the European association of national metrology institutes.
- Is involved in the European metrology research programme EPM (European Partnership on Metrology) managed by EURAMET, notably within the framework of the European research project MetSuperQ.
- Collaborates closely with the Horizon Europe project Qu-Test, which has established a federated network of experimental platforms forming an expert and independent European service infrastructure for testing and experimenting with quantum technologies, according to best practices (harmonised or even standardised), open to European industrial and academic players.
- Aims to integrate any larger European infrastructure aimed at expanding access to the testbeds, facilities and equipment needed to test and validate scientific and technological advances, and ultimately to accelerate the development of prototypes necessary for the industrial deployment of quantum technologies.
The existing metrological capabilities of the RNMF laboratories will be strengthened through the acquisition and installation of additional equipment to ultimately offer new measurement capabilities, at the highest metrological level, on the topics defined as priorities by the French National Strategy for Quantum Technologies (SNQ) : quantum computing, quantum sensing, and enabling technologies for implementing these quantum devices.
The MetriQs-France platform is primarily used for implementing the MetriQs-France programme, especially within the framework of the R&D projects MOCQUA and QUBE, through the development of reference measurement and characterisation methods for quantum computer hardware components, including qubits.
All scientific publications related to the programme are available on the HAL platform MetriQs-HUB-France.
The thematic poles of the MetriQs-France platform
In practice, the MetriQs-France platform is structured around four thematic poles reflecting the areas of expertise and competence of LNE and the RNMF. These poles concern:

- Solid-state qubits and enabling technologies (RF electronics and cryogenics).
- Very low-temperature thermometry.
- Quantum gravimeters.
- Atomic clocks.
Scientific and technical manager
- Félicien SCHOPFER, felicien.schopfer@lne.fr
Solid-state qubits and enabling technologies pole

This pole aims to develop new means of characterising components (wiring, connectors, filters, amplifiers, superconducting electronics), measurement instruments and cryogenic systems necessary for the implementation of solid-state quantum processors at very low temperatures. In the longer term, it also concerns the characterisation of qubits and small quantum processors combining a few qubits (superconducting qubits, spin qubits and emerging technologies such as flying or topological electronic qubits), with regard to the properties necessary for performing quantum calculations.
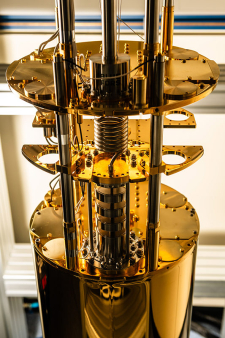
Based on existing activities in quantum and high frequency electrical metrology, the new equipment installed – dilution refrigerators integrating not least travelling wave parametric amplifiers (TWPAs), DC/LF/HF electrical and electronic instruments, Josephson arbitrary waveform synthesizer (JAWS), high frequency (HF) measurement and control instruments – will enable LNE to develop new metrology activities in support of developing quantum computers, starting with enabling technologies (cryogenic electronics in particular). In terms of service, this equipment is intended to meet the need for industrial and academic users to access controlled measurement means specific to the implementation of qubits in the perfectly controlled experimental conditions of LNE. Consequently, this equipment will be made accessible to stakeholders in the quantum ecosystem.
Thus, LNE is fully committed to the new field of metrological characterisation of qubits and enabling technologies for solid-state quantum computing. With these measurement resources and mastery of environmental conditions, LNE aims to position itself as a reference laboratory for characterising the technologies of tomorrow, supporting innovation in this field and promoting the industrialisation of these new technologies.
Pole manager
- François COUËDO, francois.couedo@lne.fr
Very low temperature thermometry pole
This pole aims to develop new means of characterising equipment in two ways:

Funded by the Ile-de-France Region (SESAME EX039201)
- Characterisation of cryogenic systems intended for the implementation of quantum technologies, particularly qubit technologies, based on the skills and infrastructure already existing at LNE-CNAM, by implementing the generation of very low temperatures (around 10 mK) and the traceability of their measurements to the International System of Units (SI) via the Provisional Low Temperature Scale of 2000 (PLTS-2000), the reference established in the laboratory.
- Development and characterisation of very low-temperature optomechanical quantum resonators for temperature quantum measurement, to apply it to measurements on qubits, with the aim of integrating sensors into the qubit chip.
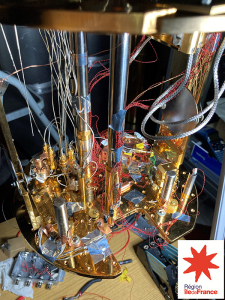
Action funded by the Ile-de-France Region (SESAME EX039201)²
This thermometry work will benefit from the laboratory’s expertise, which is ranked among the best in the world in the field. This expertise is demonstrated by the laboratory’s leading contribution to the redefinition of the kelvin in 2018, and its skills in acoustic thermometry and temperature measurement below 1 K through the measurement of the fusion pressure of helium-3. The metrology work using optomechanical techniques is part of a well-established collaboration with two CNRS laboratories, the Laboratoire Kastler Brossel (LKB) in Paris and the Centre for Nanoscience and Nanotechnology (C2N) in Saclay.
The new electronic instrumentation developed for thermometry on qubits will make it possible to access and measure the very low temperatures required for implementing quantum technologies. The developments aim, on the one hand, to provide traceability of measurements at the PLTS-2000 temperature scale (Provisional Low Temperature Scale) down to 10 mK and, on the other hand, to integrate optomechanical means of measuring temperature into the qubits. The targeted improvements concern the performance of cryogenic generation and measurement means (stability of cryostats and accuracy of temperature measurement traceable to the local reference scale) and the provision of these facilities to external users.
Pole manager
- Stéphan BRIAUDEAU, stephan.briaudeau@lecnam.net
Quantum gravimetry pole

This pole aims to develop new means of characterizing inertial sensors, gravimeters and quantum gradiometers, with reference to the LNE-OP cold atom gravimeter at the Laboratoire Temps Espace (LTE) of the Observatoire de Paris – PSL. This cold atom gravimeter, designed on the basis of atomic interferometry techniques by the LNE-OP team, a pioneer in this field, is the national reference (absolute measurement standard) in gravimetry. It is also today the most accurate and sensitive gravity measuring instrument in the world.
The development of a new optical, fiber-connected and automated bench is intended to improve and facilitate the control of the cold atom standard gravimeter placed in a specially adapted laboratory space. It will expand the service offering for characterisation and calibration of quantum gravimeters and gradiometers developed by French players, thanks to the progress made in terms of measurement performance (accuracy and sensitivity) and in terms of external services (simpler, more reliable, automated and continuous operation, more compact instrument facilitating its transportability).
These new measurement methods will be put at the service of French industrial partners who are developing increasingly efficient instruments, particularly with the deployment of quantum technologies, in response to growing demand for numerous industrial applications, such as civil engineering, mining and hydraulic prospecting, and Earth and climate sciences. In parallel, other more fundamental research projects in gravimetry will be developed within the framework of the Quantum National Research Programme, such as the QAFCA project applied to geophysics. Overall, the planned developments will enable France to maintain its independence and its global lead in gravimetry, both for reference measurements in laboratory and for industrial measurements carried out on site.
Pole manager
- Sébastien MERLET, sebastien.merlet@obspm.fr
Atomic clock characterisation pole

This pole aims, on the one hand, to improve and make reliable the time-frequency references of LNE-OP at the Laboratoire Temps Espace of the Paris Observatory – PSL in Paris and, on the other hand, to set up a service for the characterisation and calibration of oscillators and optical lattice clocks. This last activity responds to a growing demand from industrial companies and contributes to the development of quantum technologies, which require frequency references whose performances are close to the best current measurement capabilities.
Within the French National Metrology Network (RNMF) , LNE-OP is the national metrology institute for time and frequency. As such, it generates the reference time scale for France – UTC(OP), basis of French legal time – and ensures that national time and frequency references are made available to the whole of French society.

Its R&D work is fully in line with the objectives of the international time metrology community highly engaged in preparing a new definition of the second in the International System of Units (SI), for adoption by 2030. The unit of time is in fact the SI unit produced with the greatest accuracy and most units of measurement are derived from it. And with the advent of new technologies such as quantum technologies, it has become essential to redefine the SI second to improve frequency measurement references by two orders of magnitude and to be able to transfer this performance gain to measurements for characterisation of instruments or equipment based on quantum technologies, and more broadly to meet the future measurement needs (geodesy, measurement and telecommunications by satellite, geolocation, navigation, knowledge of fundamental physics, etc.).
The developments envisaged in this quantum programme rely on all the infrastructure and cutting-edge instruments existing at LNE-OP. To complement them, new equipment is being developed, such as an ultra-stable and very low noise cryogenic microwave oscillator (without consumption of liquid helium). They will improve the performance of time and frequency metrological references (oscillator stability and clock accuracy) and expand the measurement service offering for external users (more reliable operation of the benches, continuously and at lower cost).
Pole manager
- Luca LORINI, luca.lorini@obspm.fr





